In geophysics, earthquakes are vibrations or sudden settlements of the earth’s crust, caused by the sudden movement of a rock mass in the subsoil. These events, especially in highly seismic regions where there are densely populated settlements, can cause great losses of human and economic lives; seismic risk analysis therefore becomes an essential element in the design of fastening systems. In Eurocode 8 (EN 1998) the general guidelines for building regulations relating to earthquakes are defined.
The purpose of Eurocode 8 is to guarantee:
that human lives are protected
that the damage is limited
that the structures defined as important for Civil Protection remain operational
Non-collapse requirements:
Resist the seismic action of the project without local or global collapse
Preserve structural integrity and a residual bearing capacity after the event
Damage limitation requirement:
Resist the most frequent seismic action without damage
Avoid use restrictions without high costs
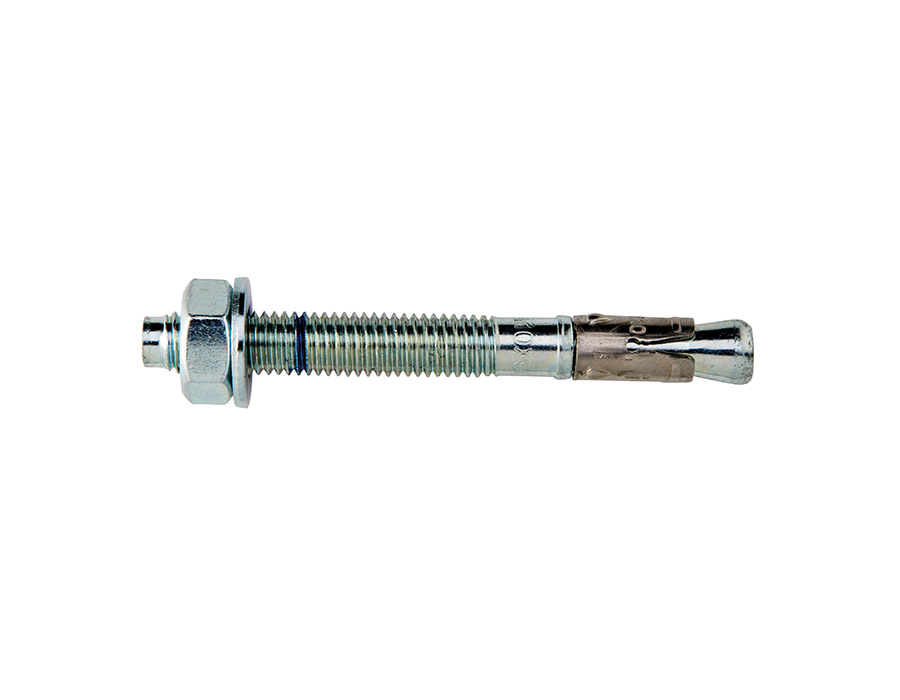
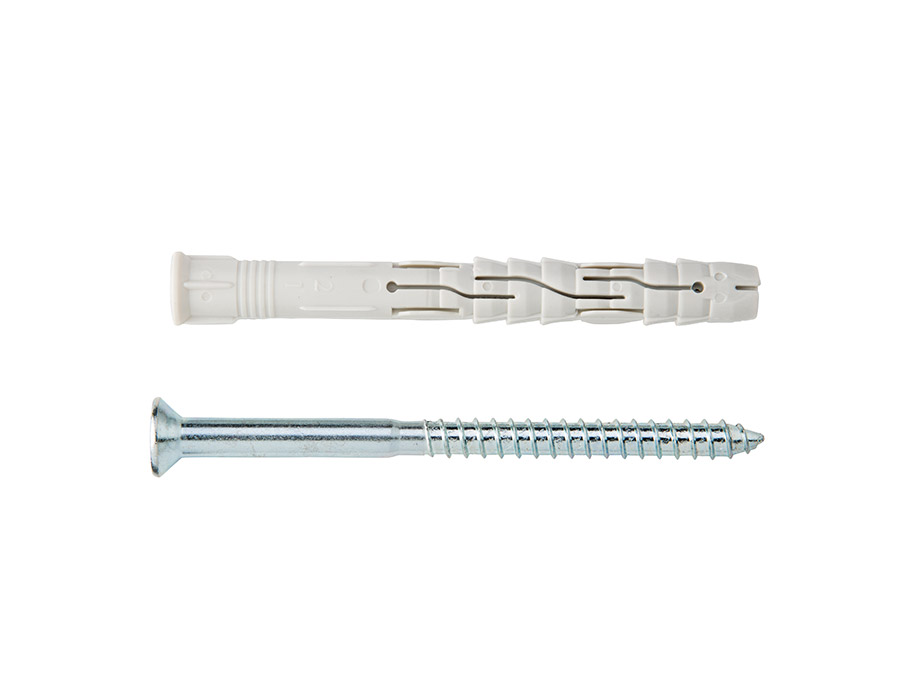
Qualification for fixing systems
Performance category C1 provides the anchor capacity in terms of strength (forces), while performance category C2 provides the anchor capacity in terms of strength (forces) and deformations. In both cases the effect of the cracking of the concrete must be taken into account. The maximum crack width considered in C1 is Δw = 0.5 mm and in C2 it is Δw = 0.8 mm.
The qualification of anchors for category C1 includes tests under pulsating tensile load and tests under alternating shear load.
The qualification of anchors for performance category C2 includes reference tests up to breaking, tests under pulsating tensile load, tests under alternating shear load as well as tests under cyclic cracking. In these tests, forces and displacements are measured continuously or at specified intervals. The qualification of anchors for category C2 requires the highest performance on the performance of anchors under seismic action when compared with category C1.
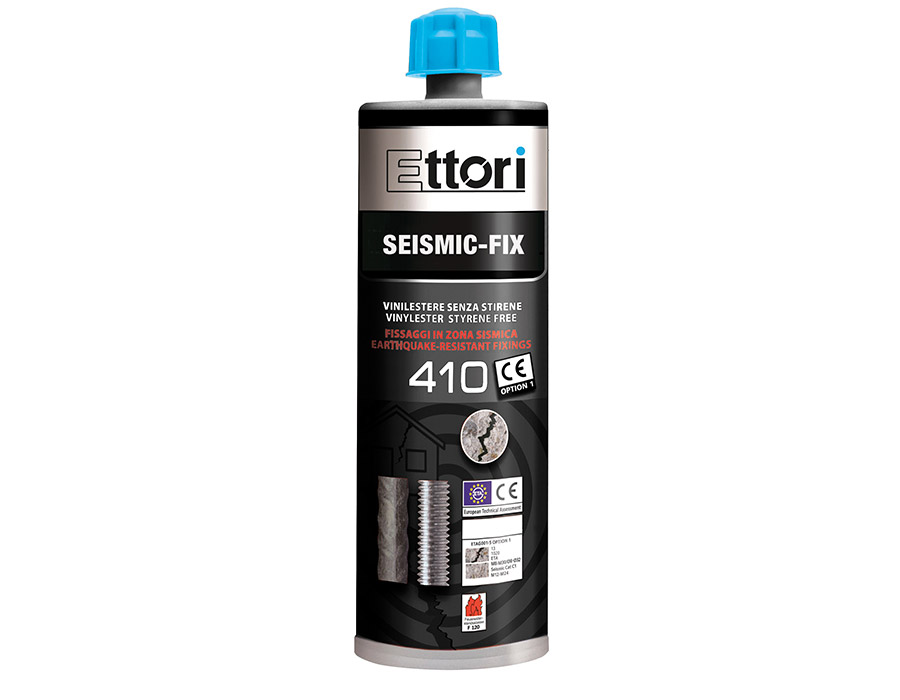
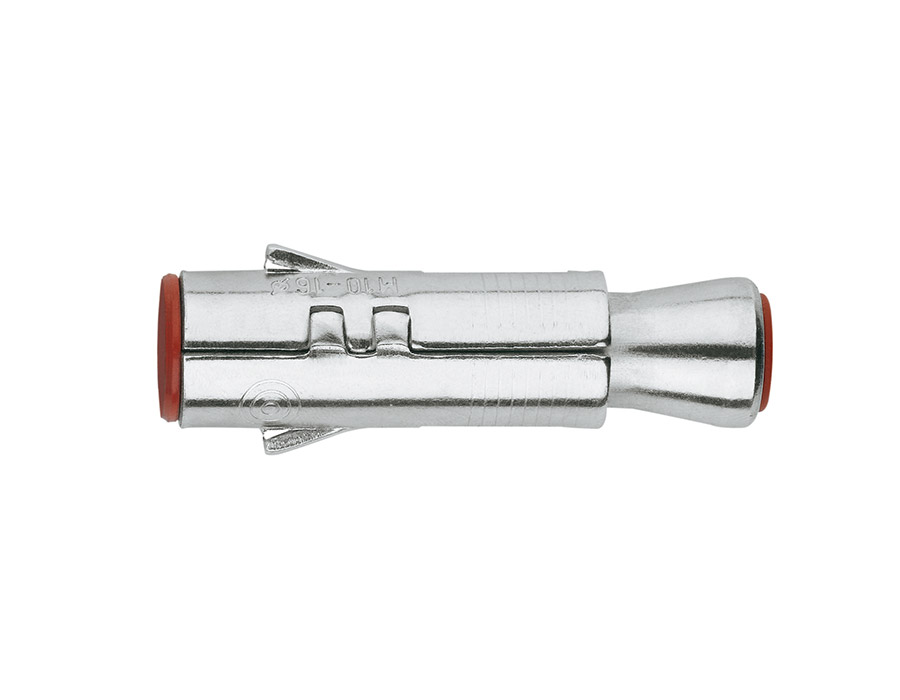
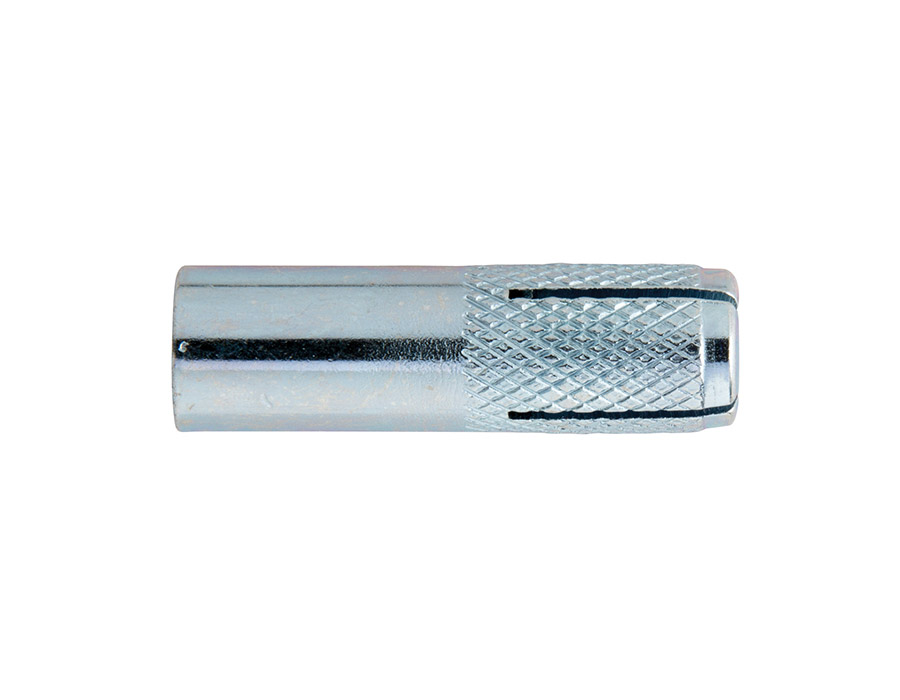
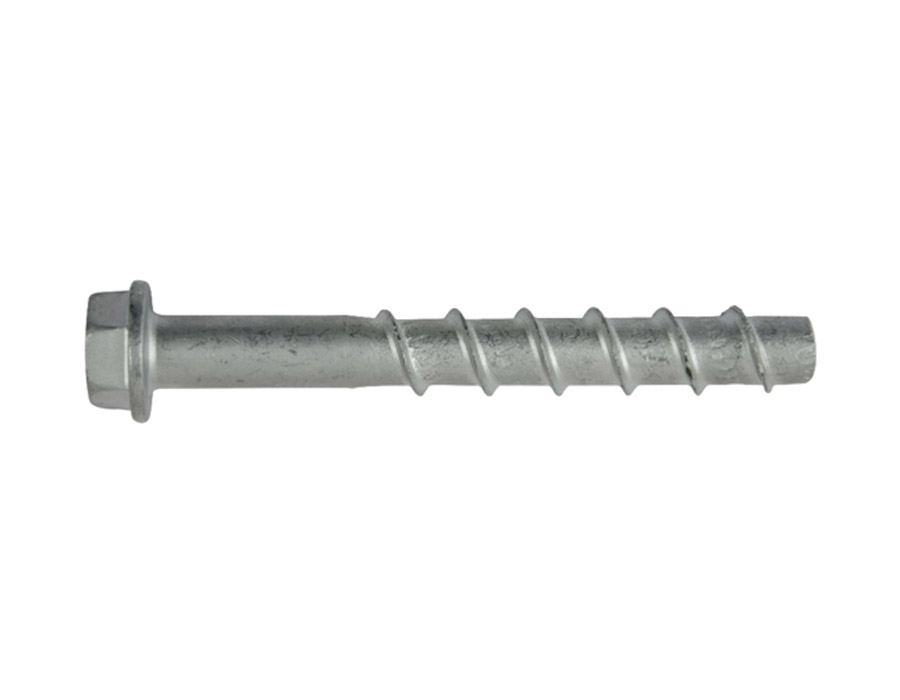
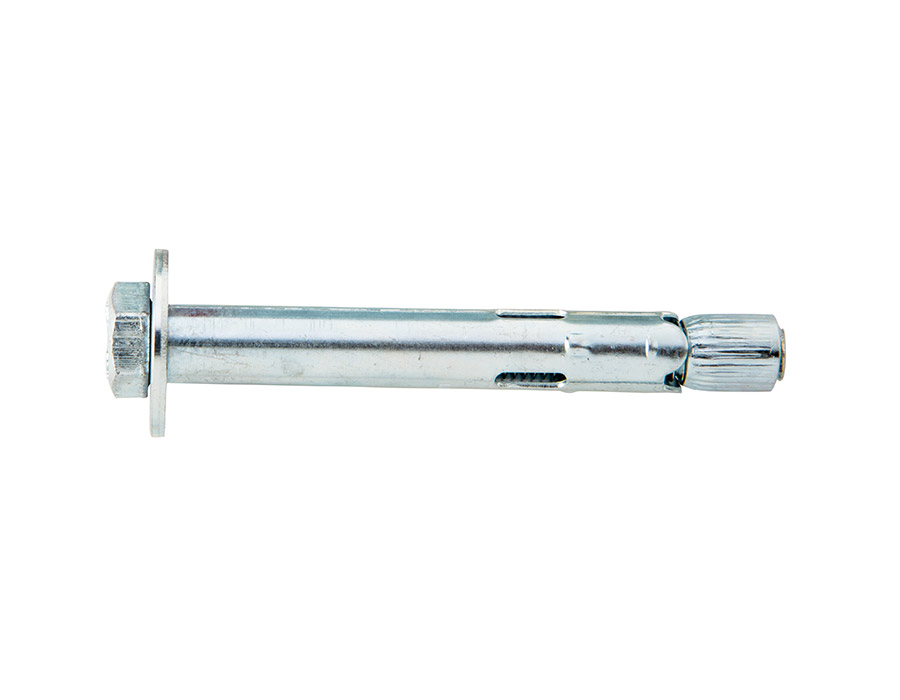
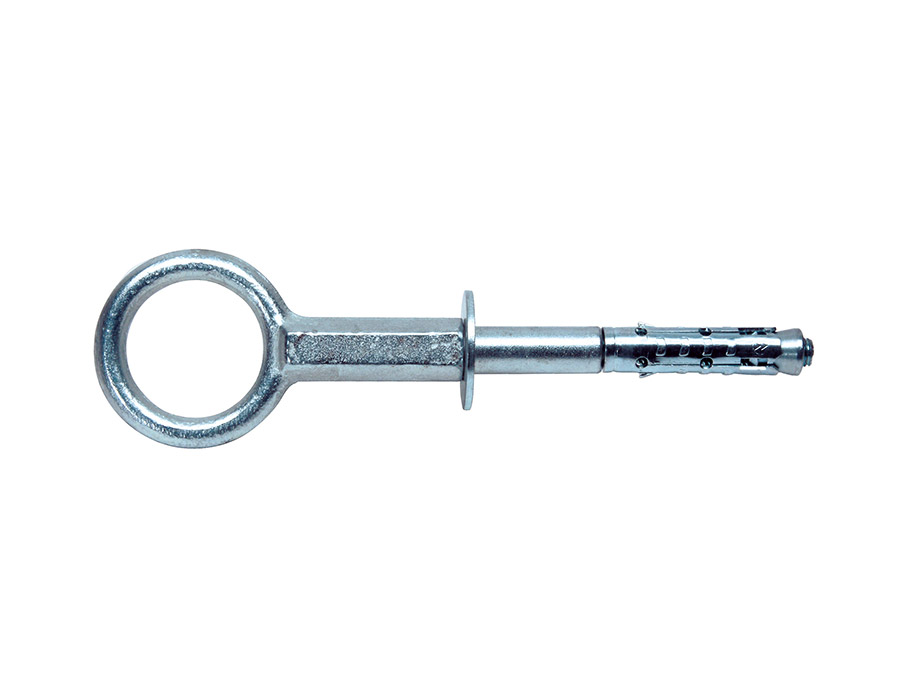
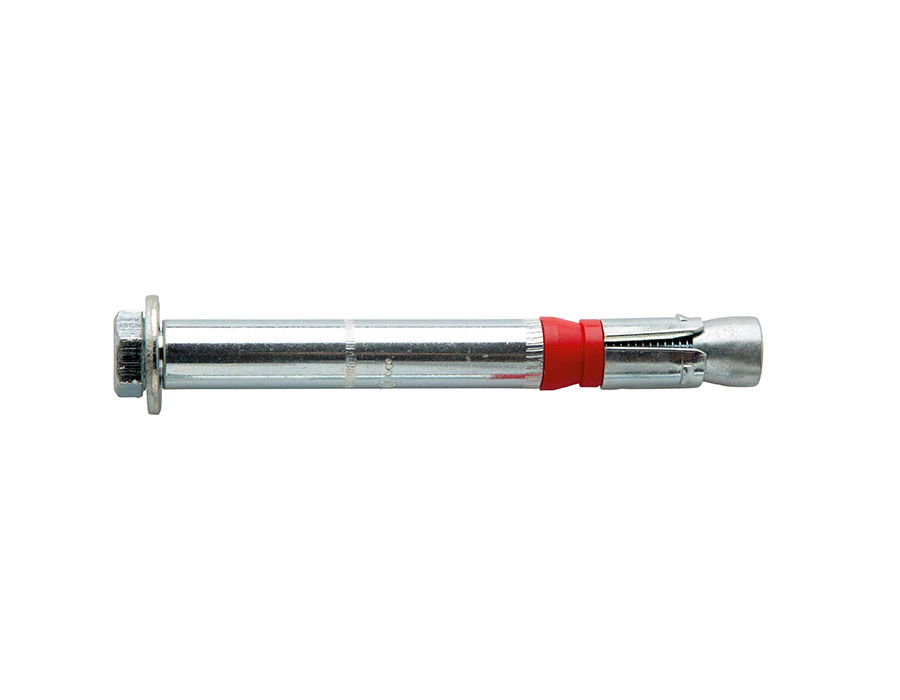
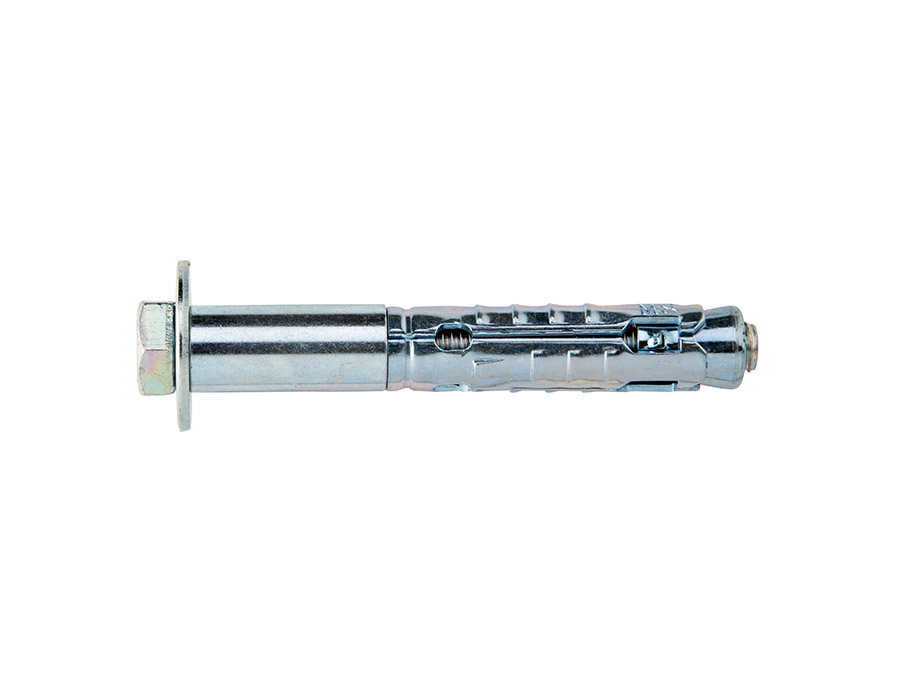
Ettori has a range dedicated to products that meet these needs: